By Damlanur Tat
As investigated on sectoral base, it can be seen that today the most common use of child labor is still in the agricultural sector. In worldwide, the sector represents a portion of 60% of child labor between 5-17 ages. Children, in this sector, are most likely the family members who have been working with parents since their childhood and are not gainfully employed. Poverty, lack of educational opportunities, inadequate agricultural technologies and cultural traditions make children engage in agricultural sector can be ranged as the reasons of high incidence of child labor in agricultural sector, which are also evaluated as dangerous for children. Agricultural sector including farming, forestry, fishing and aquaculture and animal husbandry (or livestock) in is handled one of the “dangerous” sectors for child labor1.
One of the worst forms of the child labour is the use of children in “firefights and wars” termed as “child soldier”. It’s well known that there are at least 17 countries around the world have child soldiers. By abusing the innocence, misery and naiveness of children, getting them to work or simply exploiting some as gunmen on the forefront (in the war), some as supporters in conflicts (i.e. message courier, assistant, etc) by taking advantage of the chaos that conflict/war causes is one of the issues sought to be prevented.
According to the ILO; “Commercial sexual exploitation of children” is defined as the sexual exploitation by an adult of a child or an adolescent-female or male-below 18 years of age that involves a transaction in cash or in kind to the child or to one or more third parties. The trafficking of children and adolescents for the sex trade, child sex tourism, the production, promotion and distribution of pornography involving children and the use of children in sex shows (public or private) are also covered under this title2. Studies aiming to prevent the sexual exploitation have been preceded with the objectives defined separately for the nations and regions by ILO.
In addition to above, “household chore” is another area using child labor. It’s defined as paid or unpaid domestic work done by children below the relevant minimum age either in their own homes or in the home of a third party in hazardous conditions or in slavery-like situations. Actually children working in this sector are quite hard to discern. It can be told that child labor is often hidden and hard to tackle in this area. Household chores vary from country to country and culture to culture. Unfortunately through this sector, there are standing dangers for children anywhere in the world. For example; toxic chemicals, knife, scissors etc. nipper/driller and also sexual abuse are some kinds of hazards for children. According to year 2012 data; there are 17,2 millions of children have been subjected to such kind of hazards. Unfortunately most of them are girls. Studies in worldwide and also in Turkey to prevent such exposure have been proceeded.
Migration is one of the titles should be mentioned while talking about child labor. According to UNDP data; 214 million people internationally migrated and 740 million people nationally migrated in worldwide3Children migrated legally or illegally and forced to migrate by environmental circumstances, wars and other reasons or had to be in a difficulty either alone or with his/her family in an expatriated new country are taken place in the same scope. Legal framework on this subject is promoted on several counts such as: keeping children away from any kind of discrimination, providing educational opportunity. Governments are expected to develop policies considering these children.
Mining and quarry are also areas using child labor. It’s one of the most hazardous areas in which children used by any means. Although many major developments realized until today, child labor is still coming across in Asia, in Africa, in Latin America and even in Europe.
The child labor is mostly used in some sectors and areas picked up above are involved under the category of “The Worst Forms of Child Labor”. Studies on the elimination of child labor in all these areas have been preceding for many years. 246 million children were defined as “child labor” in the year 2000 and 171 million among them were employed in hazardous works4.
Figure 1: Global trends in child labour
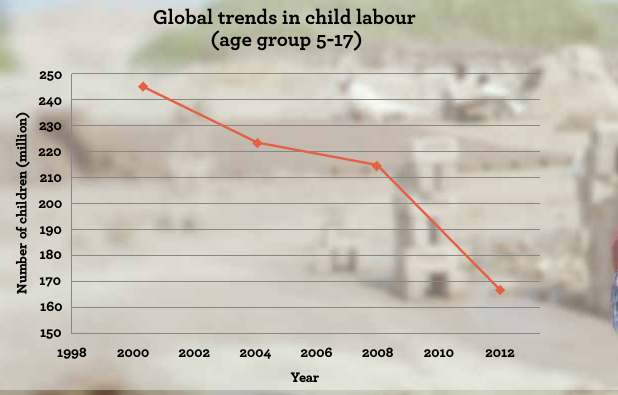
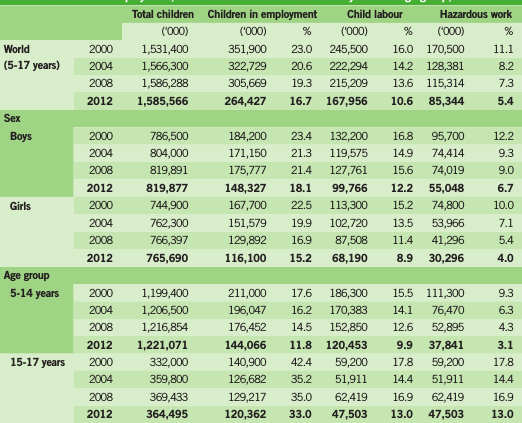
Table 1 : Children in employment, child labour and hazardous work age group, 2000-20125

Table 2. Children in employment,child labour and hazardous work by sex, 5-17 years age group, 2000-20126
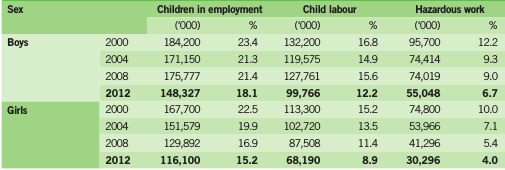
Table 3: Children in employment, child labour and hazardous work by sex and age groups, 2000-20127
As can be seen above table, great success was gained in reducing numbers of child labor of year 2000. 78 million children were removed from being child labor up to year 2012 and 246 million, the number of children in employment in the year 2000 have been decreased to one third and became 178 million. When analyzed as proportionally 40% of girls, 25% of boys were removed from being child labor8.
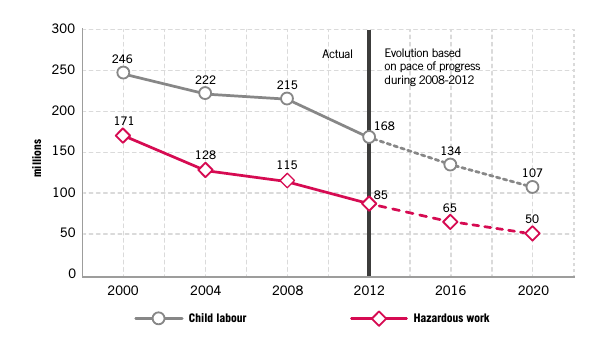
Figure 2: Number of children in child labour and hazardous work, actual 2000-2012 and levels for 2016-2020 assuming the pace of progress during 2008-20129
As can be understood above table; child labor and the use of child labor in hazardous works are expected to decrease within the next years as it was in recent years. ILO-IPEC (International Labour Organisation / International Programme on Eliminating Child Labour) and many countries’ cooperation has been the most important factor in terms of the amount decreased in child labor in recent years and of the decrease by foreseen level expected to be realized in future.
Fighting against child labor needs a long lasting effort in which all the actors, such as governments, employees, NGO’s, international and supranational organizations, teachers, families, cooperate each other. Even though many successes have been gained up to today, in many countries children are still employed in hard conditions, sold like slaves, and undeservingly maintain their life. Hopefully may the future better than today for children.
_________________
1 http://www.ilo.org
2 Guidelines on the design of direct action strategies to combat commercial sexual exploitation of children (2007)
3 UNDP, Overcoming barriers: Human mobility and development, Human Development Report 2009, New York, 2009
4 IPEC Action Against Child Labor 2012-2013, Progress and Future Priorities
5 new global report Making progress against child labour
6 New Global Report Making Progress Against Child Labour Global Estimates and Trends 2000-2012
7 New Global Report Making Progress Against Child Labour Global Estimates and Trends 2000-2012
8 New Global Report Making Progress Against Child Labour Global Estimates and Trends 2000-2012
9 New Global Report Making Progress Against Child Labour Global Estimates and Trends 2000-2012